Title: Exploring JavaScript Objects: Harnessing the Power of Data Organization
Table of contents
No headings in the article.
Exploring JavaScript Objects and Their Methods: A Comprehensive Guide
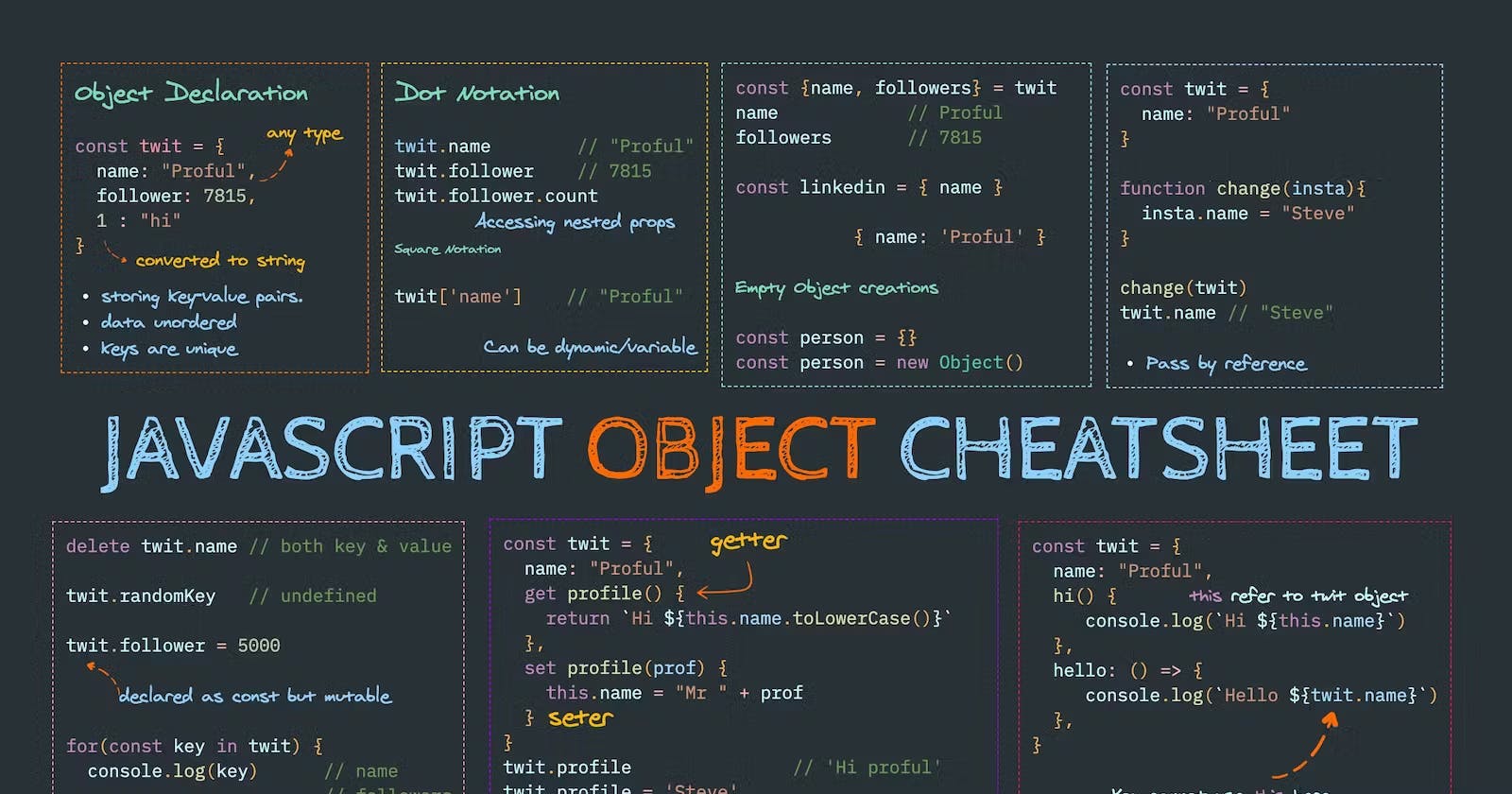
JavaScript is a versatile programming language that offers a rich set of data structures and methods to work with. One of the fundamental building blocks in JavaScript is the object, which allows you to store and manipulate data in a structured and organized manner. In this article, we will delve into JavaScript objects and explore their methods through practical examples.
Understanding JavaScript Objects
In JavaScript, an object is a collection of key-value pairs, where each value can be of any data type, including other objects. Objects provide a way to represent real-world entities, such as a person, car, or even abstract concepts. To create an object, you can use either object literal notation or the Object constructor.
Let's start with an example using object literal notation:
const person = {
name: 'John Doe',
age: 25,
profession: 'Web Developer',
};
In this example, we have created an object named person with properties such as name, age, and profession. You can access the values of these properties using dot notation or bracket notation.
console.log(person.name); // Output: John Doe
console.log(person['age']); // Output: 25
JavaScript Object Methods
Objects in JavaScript come with a set of built-in methods that allow you to perform various operations on them. These methods are pre-defined functions attached to objects and can be accessed and invoked using dot notation.
Let's explore some commonly used object methods:
Object.keys(): This method returns an array of the object's own enumerable property names.
const person = {
name: 'John Doe',
age: 25,
profession: 'Web Developer',
};
const keys = Object.keys(person);
console.log(keys); // Output: ['name', 'age', 'profession']
Object.values(): This method returns an array of the object's own enumerable property values.
const values = Object.values(person);
console.log(values); // Output: ['John Doe', 25, 'Web Developer']
Object.entries(): This method returns an array of the object's own enumerable property key-value pairs as arrays.
const entries = Object.entries(person);
console.log(entries);
// Output: [['name', 'John Doe'], ['age', 25], ['profession', 'Web Developer']]
Object.assign(): This method is used to copy the values of all enumerable properties from one or more source objects to a target object.
const target = { age: 30 };
const source = { name: 'Jane Smith', profession: 'Software Engineer' };
Object.assign(target, source);
console.log(target);
// Output: { age: 30, name: 'Jane Smith', profession: 'Software Engineer' }
Object.hasOwnProperty(): This method checks if an object has a specific property as its own property (not inherited).
console.log(person.hasOwnProperty('name')); // Output: true
console.log(person.hasOwnProperty('address')); // Output: false
Object.freeze(): This method freezes an object, preventing any modifications to its properties.
const frozenObject = Object.freeze(person);
person.name = 'Jane Smith'; // This modification will have no effect
console.log(person.name); // Output: John Doe
These are just a few examples of the numerous methods available for JavaScript objects. Understanding and utilizing these methods will empower you to manipulate objects efficiently and perform complex operations with ease.